Advertisement
Osteopathic Medicine
Of all of the natural and holistic health care disciplines, osteopathic medicine is one of the fastest growing, providing a viable and noninvasive alternative to risky surgeries or expensive diagnostic procedures. There are currently 20 osteopathic schools in the United States; the Canadian College of Osteopathy (osteopathiecollege.com) offers a five-year course of study. It is … Continued
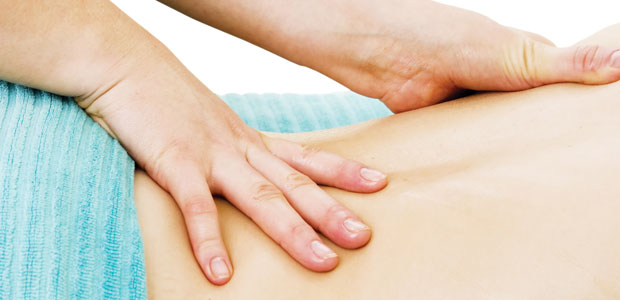
Of all of the natural and holistic health care disciplines, osteopathic medicine is one of the fastest growing, providing a viable and noninvasive alternative to risky surgeries or expensive diagnostic procedures.
There are currently 20 osteopathic schools in the United States; the Canadian College of Osteopathy (osteopathiecollege.com) offers a five-year course of study. It is only in the US, however, that doctors of osteopathy (DO) are given the right to practise as medical doctors. Osteopathic physicians in the US take the same licensing exams and boards and practise as MDs, using an integrative approach to health and wellness. In the US, it is estimated that over 100 million patients visit a DO yearly.
Beyond Bones
The term osteopathy comes from the Greek osteon (bone) and pathos (suffering); literally, it means suffering of the bone. However, osteopathic doctors are far more than bone specialists. The current practice of osteopathic medicine encompasses a diagnostic and treatment approach that corrects biochemical imbalances within the body with hands-on techniques and a holistic approach.
A doctor of osteopathy focuses on finding health, rather than treating illness. According to osteopathic theory, correction of spinal imbalances is thought to restore and maintain the functioning of the nervous and musculoskeletal system. The DO uses his or her hands to diagnose and treat imbalances with osteopathic manipulative treatment. The DO’s highly skilled sense of touch (known as palpation) allows for detection of the texture of tissues and structure of the body, as well as blockages in the flow of fluids or decreases in range of motion. The osteopath gently applies a precise amount of force to promote healthy movement of muscle and tissue and release any compression in bones or joints. The osteopath’s role is to “set” the body in order for it to heal itself.
Whole Healing
Osteopaths believe that the body is a self-regulating and self-healing organism, and when interference is removed, the body will return to its normal state of health and wellness. This natural tendency for healing and repair is referred to as the homeostatic nature of the body. In addition to osteopathic manipulative treatment, dietary counselling and stress management are also part of the osteopath’s whole mind-body approach.
Osteopathic doctors believe that past and current experiences play a significant role in overall physical and mental health. Each patient is treated as an individual, and no two treatments will be identical. In addition, osteopaths tend to spend a significant amount of time with each patient, with appointments lasting approximately an hour. An osteopath can treat a variety of conditions ranging from headaches and lower back pain to indigestion and fatigue.
Complementary Medicine
In recent years, the large gap between conventional medicine and natural medicine has begun to narrow. At the forefront of this coming together is osteopathy and its principles of treating the body as a whole, self-healing, and self-regulating organism.
Unity for Wellness
Osteopathic medicine was first practised by Andrew Taylor Still, MD, in 1874. After losing three children to meningitis, Dr. Still decided to develop a system of medical care that promoted the body’s innate ability to heal itself. His concept of health and medicine was based on wellness and on the unity of all parts of the body.




